Objectives
In this lab, we will look at Data Definition.
- Use CREATE, ALTER and DROP statements.
Data Defintion
So far we have performed SELECT statements on existing tables in the Library and Movie databases. We have also executed INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements.
The above 4 statements are DATA MANIPULATION statements.
We are now going to create a new database and create tables within it. The commands we will look at are DATA DEFINITION commands (statements):
- CREATE (database/table).
- ALTER (add, delete, modify table).
- DROP (database/table).
Creating a database
To create a database (also known in MySQL as a schema) we can either of the following commands:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS database_name;CREATE SCHEMA IF NOT EXISTS schema_name;Whether we enter CREATE DATABASE or CREATE SCHEMA here, the result is the same. CREATE SCHEMA is a synonym for CREATE DATABASE as of MySQL 5.0.2.
The IF NOT EXISTS part of the statement is optional, and checks whether the database you are creating already exists. If this is the case,
MySQL will ignore the whole statement and it will not create any new object (database or schema or table). The database name you choose must be unique
on your system.
To drop a database, execute either of the following commands:
DROP DATABASE database_name;DROP SCHEMA schema_name;Creating a table
The following illustrates the syntax of the CREATE TABLE statement:
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name(
column_list
) engine=table_type;Let's examine the syntax in greater detail:
- First, you specify the name of table that you want to create after the CREATE TABLE clause. The table name must be
uniquewithin the database. As before, the IF NOT EXISTS part of the statement checks if the table already exists, and if so, no new table will be created. - Second, you specify a list of columns for the table in the column_list section. Columns are separated by a comma (,).
We will show you how to define columns in more detail in the next section. - Third, you may specify the storage engine for the table in the engine clause. You can use any storage engine such as InnoDB, MyISAM, Memory (formerly known as HEAP), EXAMPLE, CSV, BLACKHOLE, ARCHIVE, MERGE, or FEDERATED. If you don't explicitly declare the storage engine, MySQL will use InnoDB by default.
InnoDB became the default storage engine since MySQL version 5.5. InnoDB brings many benefits of relational database management system such as ACID transaction, referential integrity and crash recovery. In the previous versions, MySQL used MyISAM as the default storage engine.
For more information, see: Alternative Storage Engines
Defining columns
To define a column for the table in the CREATE TABLE statement, you use the following syntax:
column_name data_type[size] [NOT NULL|NULL] [DEFAULT value]
[AUTO_INCREMENT][] denotes optional.
The most important components of the syntax above are:
- column_name specifies the name of the column. Each column must be always associated with a specific data type and the size e.g. VARCHAR(255).
- NOT NULL or NULL indicates that the column accepts a NULL value or not.
- DEFAULT value is used to specify the default value of the column.
- AUTO_INCREMENT indicates that the value of column is increased by one whenever a new record is inserted into the table. Each table can have one and only one AUTO_INCREMENT column.
MySQL data types 1
MySQL data types can be grouped into three main categories; text, number and date/time.
TEXT TYPES

- The ( ) brackets allow you to enter a maximum number of characters will be used in the column.
- CHAR and VARCHAR are the most widely used types. CHAR is a fixed length string and is mainly used when the data is not going to vary much in its length. VARCHAR is a variable length string and is mainly used when the data may vary in length.
- CHAR may be faster for the database to process considering the fields stay the same length down the column. VARCHAR may be a bit slower as it calculates each field down the column, but it saves on memory space.
- Using both a CHAR and VARCHAR option in the same table, MySQL will automatically change the CHAR into VARCHAR for compatibility reasons.
- BLOB stands for Binary Large OBject. Both TEXT and BLOB are variable length types that store large amounts of data. They are similar to a larger version of VARCHAR. These types can store a large piece of data information, but they are also processed much slower.
- BLOB values are treated as binary strings (byte strings). They have the binary character set and collation, and comparison and sorting are based on the numeric values of the bytes in column values. TEXT values are treated as non-binary strings (character strings). They have a character set other than binary, and values are sorted and compared based on the collation of the character set. Blob datatypes stores binary objects like images while text datatypes store text objects like articles of a webpage.
MySQL data types 2
NUMBER TYPES

- The integer types have an extra option called UNSIGNED. Normally, the integer goes from a negative to positive value. Using an UNSIGNED command will move that range up so it starts at zero instead of a negative number.
- Specifying a numeric field as smallint (for example) will allow numeric values to be stored upto a maximum value of 32767 (or 65535 for unsigned). There is no advantage specifying a value with the numeric data type (for example - smallint(4)). The optional display width specifier (for integer data types) is only applicable when using zerofill and has nothing to do with the internal size (in bytes) of the integer data type.
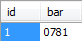
create table foo
(
id int auto_increment primary key,
bar smallint(4) unsigned zerofill not null default 0
);insert into foo (bar) values (781);select * from foo;This will return:
MySQL data types 3
DATE TYPES
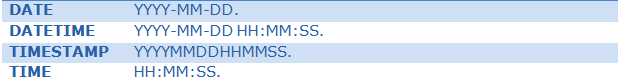
Enum
ENUM is a data type in MySQL. An ENUM is a string object with a value chosen from a list of permitted values that are enumerated explicitly in the column specification at table creation time.
CREATE TABLE Foo
( color ENUM('red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow')
);This column allows you to store one of the values in the enum list, but no other value.
Keys
Primary key
If you want to set particular columns of the table as the primary key, you use the following syntax:
PRIMARY KEY (col1,col2,...)Foreign key
To set a foreign key, we explicitly link an attribute in one table with the primary key value of another table.
For Example: From our library script
create table Book (
ISBN varchar(15) not null,
title varchar(50) not null,
publisher varchar(30),
publishedDate date,
category varchar(30),
price decimal(5,2),
primary key (ISBN)
);create table BookCopy(
copyId int auto_increment not null,
ISBN varchar(15) not null,
dateAcquired date not null,
dateDestroyed date,
primary key (copyId),
constraint fk_book foreign key(ISBN) references Book(ISBN)
on update cascade
on delete no action
);In the foreign key clause you may specify what is to happen to the foreign key value if the primary key is updated or deleted. The options are:
- cascade (all related foreign key values are updated or deleted when a primary key value is updated or deleted respectively).
- no action (if there are related foreign key values then the primary key value cannot be updated or deleted).
- set null (all related foreign key values are set to null if the primary key value is updated or deleted).
Alter or Drop a table
To check what tables (if any) exist in a database, enter the following command:
SHOW tables;You should see tables MANUFACTURER and CAR. To see a description of the table, CAR, enter:
DESCRIBE car;or
DESC car;Alter a table
To alter a table, you can use the any of the following commands:
Add a column:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD column_name datatypeDelete a column:
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN column_nameModify a column:
ALTER TABLE table_name
CHANGE COLUMN old_column_name new_column_name datatypeor
ALTER TABLE table_name
MODIFY COLUMN column_name datatypeDrop a table
To drop a table, you can use the following command:
DROP TABLE table_name;Note that if you try to delete a table that has related records in another table, you will receive an error message.
Example - Data Definition
The following example demonstrates the creation of a database called Car_Sales and a table called Manufacturer.
- Once a database is created and before you can create a table you must tell MySQL which database you want to use, so we need to enter (USE database_name;).
- The primary key of the manufacturer is an integer and is set to
auto incrementmeaning that each manufacturer will automatically be assigned a unique number by the system. The primary key constraint itself means that the field cannot be blank and the value it contains must be unique within that table. - Note that some other attributes are also set to
not nullmeaning that those fields cannot be blank.
Enter the following commands:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS CAR_SALES;USE CAR_SALES;CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS MANUFACTURER
(
MCODE INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
MNAME ENUM('Audi', 'BMW', 'Opel', 'Volkswagen', 'Peugeot', 'Renault', 'Alfa Romeo', 'Ford', 'Hyundai', 'Kia',
'Saab', 'SsangYong', 'Honda', 'Lexus', 'Mazda', 'Mitsubishi', 'Nissan', 'Suzuki', 'Toyota') NOT NULL,
MCOUNTRY VARCHAR(20),
PRIMARY KEY(MCODE)
);Foreign keys
We will now create a second table called Car, which is related to the Manufacturer table. We will add a foreign key constraint that means that we
cannot place a manufacturer code in the car table, unless a related code exists in the manufacturer table.
Note that the field names (primary key field and related foreign key field) do not need to be the
same, but the data type (and size, if relevant) must be the same.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS CAR
(
REG VARCHAR(15),
MODEL VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
COST DOUBLE(8,2),
MCODE INT,
PRIMARY KEY(REG),
CONSTRAINT FK_MCODE FOREIGN KEY(MCODE)
REFERENCES MANUFACTURER(MCODE)
ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE SET NULL
);We will now alter a column (cost) in the car table:
ALTER TABLE car MODIFY COLUMN cost DECIMAL(8,2);Example - Data Manipulation
Insert the following records into the MANUFACTURER table:
INSERT INTO MANUFACTURER (MNAME, MCOUNTRY) VALUES
('Audi','Germany'),
('BMW','Germany'),
('Opel','Germany'),
('Volkswagen','Germany'),
('Peugeot','France'),
('Renault','France'),
('Alfa Romeo','Italy'),
('Ford','USA'),
('Hyundai','South Korea'),
('Kia','South Korea'),
('Saab','Swedan'),
('SsangYong','Swedan'),
('Honda','Japan'),
('Lexus','Japan'),
('Mazda','Japan'),
('Mitsubishi','Japan'),
('Nissan','Japan'),
('Suzuki','Japan'),
('Toyota', 'Japan');Insert the following records into the CAR table:
INSERT INTO CAR VALUES
('141-KK-345','i30',20760, 9),
('11-WD-1876','i35',14500, 9),
('151-KK-100','Astra',24800, 3),
('12-WX-222','Corolla',19870, 19),
('142-WD-7811','Vectra',28900, 3),
('08-KK-1234','Polo',6500, 4),
('10-WX-9875','Golf',9500, 4);;
Exercise
Create a new table called CUSTOMER, with the following attributes:
- customerId (int auto increment)
- fName (variable character, size 15)
- lName (variable character, size 15)
emailAddress (variable character, size 40)
Primary key: customerId
Create a new table called VIEWINGS, with the following attributes:
- customerId (same definition as in the CUSTOMER table)
- reg (same definition as in the CAR table)
- viewingDate (date)
comments (variable character, size 250)
Primary key: customerId, reg
Foreign key: customerId (related to CUSTOMER table)
Foreign key: reg (related to CAR table)
Add cascade update and delete constraints for both of the foreign key values.
Insert 2 CUSTOMER records and 5 VIEWINGS records. Remember when inserting records into the VIEWINGS table, the customerId value must match a value from the CUSTOMER table and the reg value must match a value from the CAR table.
Write select statements for each of the following:
- Return the car model, viewingDate and comments for all viewings.
- Return the customers full name, car model, viewingDate and comments for all viewings.
Solutions
Solutions for the exercises in this lab are available here: Week6.zip